Measuring range – ifm electronic RM3001 Benutzerhandbuch
Seite 49
49
Measuring range
The measuring range is defined by the parameter "Total measuring range in measuring units". The
encoder has two different operating modes, depending on the specified measuring range. When the
encoder receives a parameter message, it checks the scaling parameters for binary scaling. If binary
scaling is detected, the encoder selects operating mode A (see following explanation). If not, operating
mode B is selected.
A. Cyclic operation (binary scaling)
Measuring mode A is used if the encoder functions with 2
x
number of revolutions (number of revolutions
2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048 and 4096).
If the desired measuring range is equal to the specified singleturn resolution x 2
x
(with x
≤
12), the encoder
operates in endless cyclic operation ( 0 – max. position value – 0 – max. position value). If the position
value of the encoder exceeds the maximum value (measuring range 1) by a rotation of the axis to be
measured, the encoder indicates 0 as position value again.
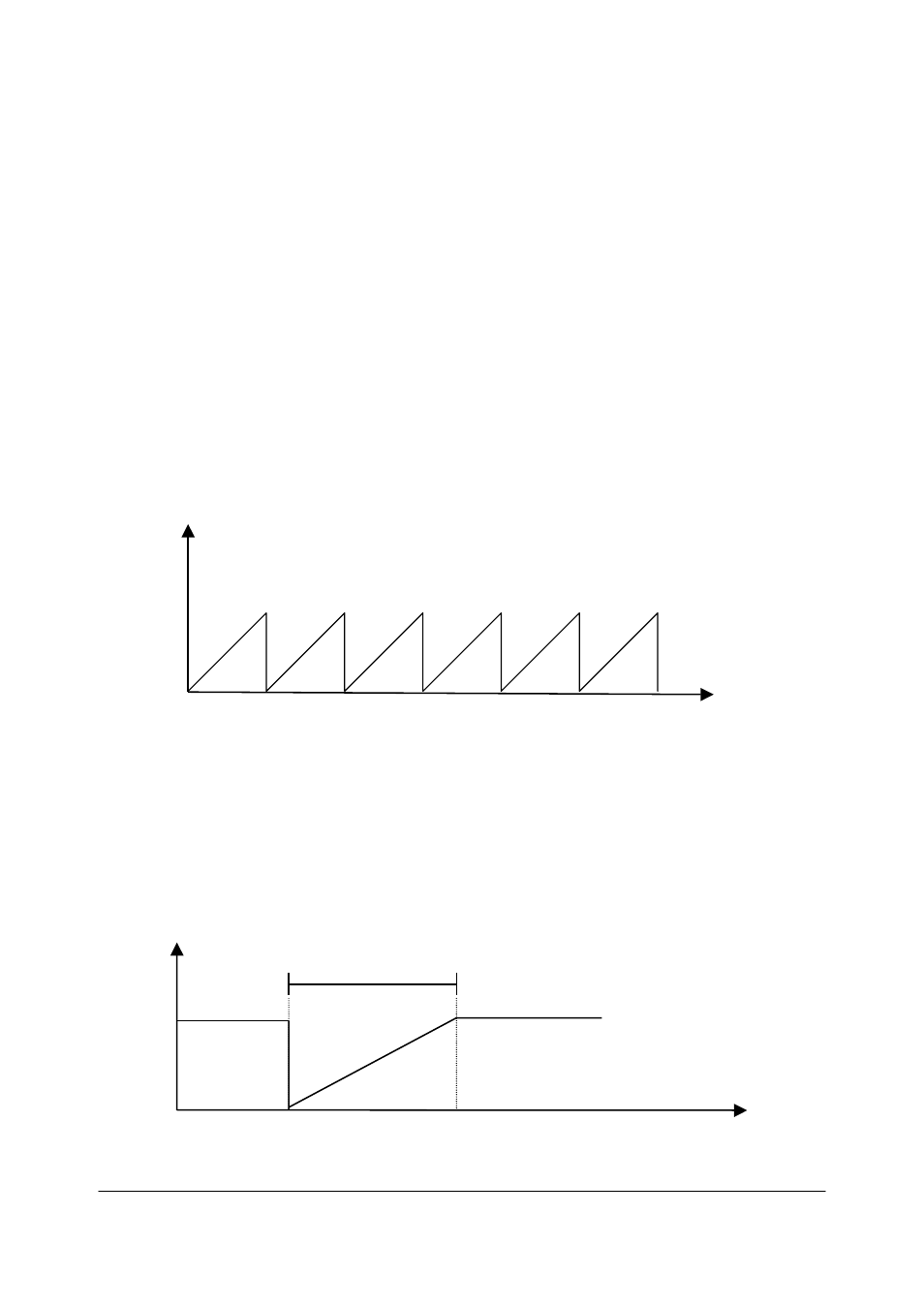
Example of a cyclic scaling:
Measuring units per revolution
= 1.000
Total measuring range
= 32.000 (2
5
= number of revolutions 32)
position
32.000
0
measuring range
B. Non-cyclic operation
If the measuring range is used to limit the value range of the encoder to a value other than the specified
singleturn resolution * 2
x
, the output position value is limited within the operating range. If the position
value exceeds the maximum value (measuring range 1) or falls below 0 by a rotation of encoder, the
encoder indicates the value of the measuring range. See figure below.
Example of non-cyclic scaling:
Measuring units per revolution
= 100
Total measuring range
= 5.000 (number of revolutions 50)
scaled total range
5.000
position
0
0
MAX
measuring range